Abscess is a localized collection of pus, which forms as the body’s immune system responds to an infection. Abscesses can occur anywhere in the body, but they are most common in the skin, soft tissues, organs, or even within body cavities like the brain or lungs. The pus within an abscess is made up of dead tissue, bacteria, and white blood cells that were dispatched to fight the infection.
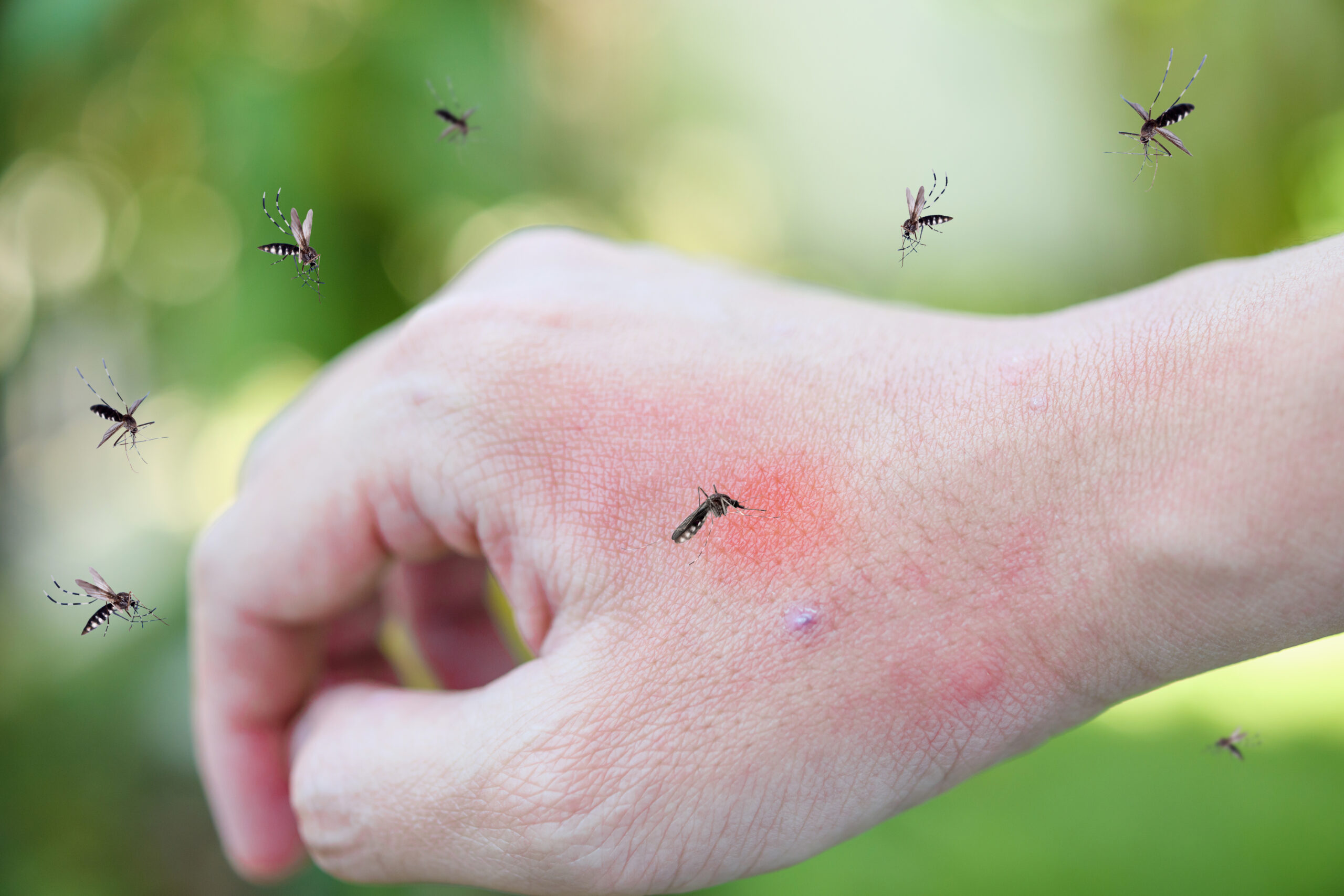
Abscesses are generally caused by infections, and they form as a result of the body’s immune response to these pathogens. Some common causes include:
- Bacterial Infections
- Injury or Trauma
- Blocked Glands or Ducts
- Chronic Conditions
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
- Immune Response
Symptoms of Abscesses
The symptoms depend on the location and severity of the abscess, but common signs include:
- Pain and tenderness around the affected area.
- Redness and swelling in the skin or surrounding tissues.
- Warmth to the touch (as the body increases blood flow to the infection site).
- Pus or drainage (a thick, often yellow or green fluid) if the abscess ruptures or is drained.
- Fever and chills (in cases of systemic infection).




